Guarding the Gates
 Cyber threats are a serious and growing problem for businesses of all sizes and sectors. Cyberattacks can cause significant financial losses, reputational damage, operational disruption, legal liability, and even physical harm. Look what happened to MGM Resorts this week.
Cyber threats are a serious and growing problem for businesses of all sizes and sectors. Cyberattacks can cause significant financial losses, reputational damage, operational disruption, legal liability, and even physical harm. Look what happened to MGM Resorts this week.
On September 10th, 2023, MGM Resorts International, a company in the casino-hotel industry, fell victim to a ransomware attack orchestrated by the ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware group. The hackers encrypted over 100 ESXi hypervisors after the company took down its internal infrastructure. Now that’s a bad day for MGM Resorts!
Cybersecurity experts are shaking their heads in awe at the preferred technique of these ransom gangs: social engineering. They’ve mastered it to an almost comical degree! ALPHV, for instance, proudly claimed it only took them a mere 10 minutes to sneak into MGM’s system. How did they do it? By spotting an MGM tech employee on LinkedIn and casually ringing up the company’s support desk – talk about efficiency! As for Scattered Spider, they gained entry to Caesars’ system by skillfully outsmarting an unsuspecting employee at a third-party vendor. It’s like these hackers have a master’s degree in “The Art of Sneakiness.”
A report from the World Economic Forum reveals that there was a 156% increase in global cyberattacks during the second quarter of 2023 when compared to the initial three months of the year.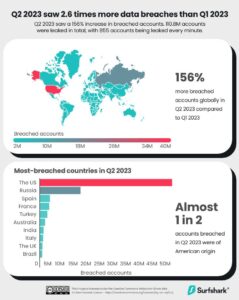
Some of the most common cyber threats that businesses face:
- Ransomware: This is a type of malware that encrypts the victim’s data and demands a ransom for its decryption.
- Phishing: This is a type of social engineering attack that uses fraudulent emails or websites to trick the recipient into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links or attachments.
- Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS): This is a type of attack that floods the target’s network or server with overwhelming amounts of traffic, rendering it unavailable or slow for legitimate users.
- Data breaches: This is a type of incident that involves unauthorized access to or disclosure of the business’s sensitive data, such as customer records, employee information, trade secrets, intellectual property, or financial data.
How can businesses protect themselves from cyber threats?
- Implement a robust cybersecurity strategy that aligns with the business goals and objectives, and covers all aspects of prevention, detection, response, and recovery.
- Educate and train the employees on cybersecurity awareness and hygiene, such as how to recognize and avoid phishing emails, how to use strong passwords and multifactor authentication, how to secure their devices and networks, and how to report any suspicious activity or incident.
- Update and patch the software and hardware regularly to fix any vulnerabilities or bugs that could be exploited by hackers.
- Use encryption and backup solutions to protect the data in transit and at rest, and to ensure its availability and integrity in case of an attack.
- Deploy security tools and solutions such as antivirus software, firewalls, VPNs, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), web application firewalls (WAF), endpoint detection and response (EDR), etc.
- Monitor and audit the network and system activity for any anomalies or signs of compromise.
- Establish a clear incident response plan that defines the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders, the communication channels and protocols, the escalation procedures, the containment and remediation actions, and the lessons learned and improvement measures.
Cyber threats are like that annoying party crasher you can’t ignore; businesses simply can’t afford to pretend they’re not there! But fear not, by embracing these best practices, companies can beef up their cybersecurity game, become as resilient as a rubber chicken, and safeguard their assets, reputation, and customers from those pesky cyber troublemakers.





